 Areas on the earth that or cold enough to change water into solid ice or snow are known as 'Cryosphere's' It derives from the Greek word 'kryos' meaning cold. These regions of our planet have a great influence on the worlds climate. When scientist refer to the cryosphere they mean they are referring to areas where temperatures allow water to freeze into its solid form. These main areas are know as the North Pole; The Arctic & The South Pole; The Antarctic. Both areas are monitored by scientists but the North Pole is covered by a cold ocean where sea ice grows in the winter and shrinks in summer. Frozen ground and permafrost ring the Arctic Ocean. Glaciers, snow, and ice cover the nearby land, including a thick sheet of snow and ice covering Greenland. The Arctic Ocean area is also surrounded by land providing an isolated area that captures the effects of wind and ocean currents from global weather patterns. With these combinations scientist are able to form a real insight into the way this hostile environment is reacting to worldly atmospheric changes. SNOW Snow is precipitation made up of ice crystals. When cold temperatures and high humidity levels combine in the atmosphere, snow crystals form. As long as air temperature remains below freezing, the crystals will fall to the Earth as snow. Snow:
Ice forms when temperatures drop below the freezing point and liquid water becomes a solid, creating a tightly bonded substance. Ice is a key ingredient in glaciers, sea ice, ice shelves, icebergs, and frozen ground. Naturally occurring ice:
SEA ICE Sea ice forms when water in the oceans is cooled to temperatures below freezing. Most sea ice forms in the Arctic and Antarctic Oceans.
GLACIERS Glaciers are thick masses of ice on land. The ice has built up from many seasons of snowfall. Glaciers move downhill very slowly.
Muir Glacier, located in Glacier Bay, Alaska, photographed by W. Field in Aug. 1941 (left) and B. Molnia in Sep. 1976 (middle) and Aug. 2004 (right). Note how the glacier has retreated to expose rock in 1976 that has since become lush vegetation in 2004. The glacier has retreated so much that it is hardly visible in the 2004 photo. —Credit: National Snow and Ice Data Center (comp.). 2002, updated 2009. Glacier Photograph Collection. Boulder, Colorado USA: National Snow and Ice Data Center. ICE SHELVES & ICEBERGS Ice shelves are platforms of ice that form where ice sheets and glaciers move out into the oceans. Ice shelves exist mostly in Antarctica and Greenland, as well as in the Arctic near Canada and Alaska. Icebergs are chunks of ice that break off glaciers and ice shelves and drift in the oceans. Ice shelves and icebergs:
FROZEN GROUND Frozen ground is soil or rock in which part or all of the water has frozen. If the ground is frozen all year long, we call it "permafrost," or permanently frozen ground. Frozen ground:
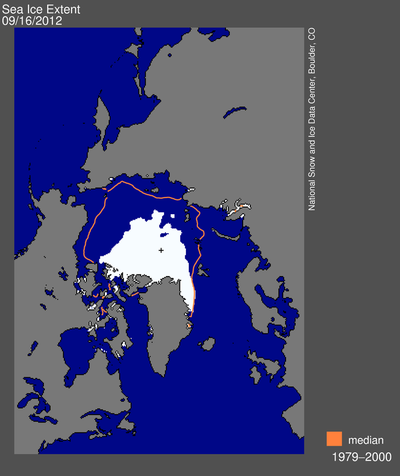
'The Arctic cold season usually begins in September and ends in March. Monitoring winter sea ice is important to understanding the state of the sea ice. Scientists have found that Arctic sea ice has been recovering less in the winter, meaning the sea ice is already "weak" when the summer melting season arrives. A possible cause is that the underlying ocean is warmer.' (http://nsidc.org/about accessed 17/3/17) The physical materiality of water in its frozen sate within these regions is in a delicate and sensitive position. Within our humbled lives we take for granted the process of freezing and how it enables us to sustain and preserve but fail to recognise the importance of this process as a means to sustain life. The fragility of the freezing process is palpable and gives rise to pure aesthetics of change from solid form to non existence.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
MA Creative Practice
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
